Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid - Get the best of two worlds
A hybrid cloud platform gives organizations many advantages—such as greater flexibility, more deployment options, security, compliance, and the ability to get more value from their existing infrastructure. When computing and processing demand fluctuates, hybrid cloud computing gives businesses the ability to seamlessly scale up their on-premises infrastructure to the public cloud, which is capable of handling any overflow—without giving third-party datacenters access to the entirety of their data. Organizations gain the flexibility and innovation the public cloud provides by running certain workloads in the cloud, while keeping highly sensitive data in their own datacenter to meet client needs or regulatory requirements.
This not only allows companies to scale computing resources— but it also eliminates the need to make massive capital expenditures to handle short-term spikes in demand, as well as when the business needs to free up local resources for more sensitive data or applications. Companies will pay only for resources they temporarily use instead of having to purchase, program, and maintain additional resources and equipment that may otherwise remain idle over long periods of time.
Advantages of the hybrid cloud:
- Control—your organization can maintain a private infrastructure around sensitive assets or for workloads that require low latency.
- Flexibility—you can take advantage of additional resources in the public cloud whenever you need them.
- Cost-effectiveness—with the ability to scale to the public cloud, you only pay for extra computing power when needed.
- Access to advanced services - cloud providers offer advanced services such as AI, Cognitive Services, IOT Management hubs and hundreds more, all available within a hybrid model.
- Ease—transitioning to the cloud doesn’t have to be overwhelming because you can migrate gradually by phasing in workloads over time.
Secure - are you sure?

The Cyber security assessment includes a detailed IT cyber security report, in which the current situation and the possible vulnerabilities are described. A typical report is 30-40 pages, and a short presentation will also be completed to summarize the findings and allow Q&A’s
Stay in the loop
Hybrid Cloud Computing
A hybrid cloud is a type of cloud computing that is derived from 4 general cloud options, it combines on-premises infrastructure or a private cloud with a public cloud. In general, you can define hybrid clouds as an IT Architecture that contains some degree of workload orchestration and management across two or more environments, where one of the cloud environments is private.
Many organizations choose a hybrid cloud approach due to business imperatives, such as meeting regulatory and data sovereignty requirements and taking full advantage of on-premises technology investments, whilst combining this with the vast amount of technology solutions available in the public cloud. Companies with uneven load patterns and regular peak loads also prefer the fast scaleup/scale down models of public clouds.
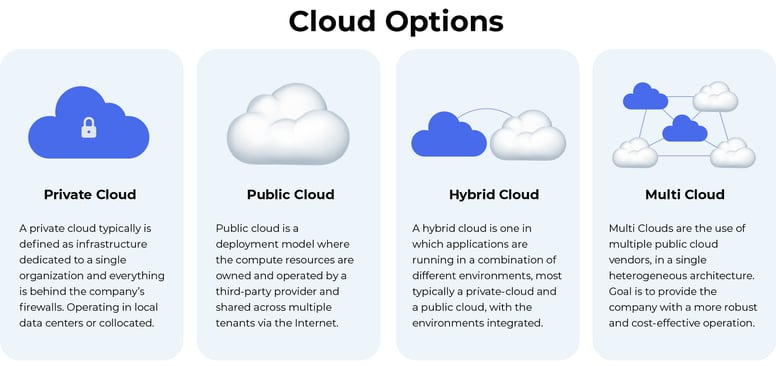
Understanding your deployment options — Public cloud, private cloud, hybrid cloud or multi-Cloud?
There’s no one type of cloud computing that’s right for everyone, and the requirements can also change over time which will require a move to a different model. Several cloud computing models, types, and services have evolved to meet organisations' rapidly changing technology needs. There are 4 different ways to deploy cloud services: on a public cloud, private cloud, hybrid cloud or via a multi-cloud. The ideal deployment method depends on your business needs, and there are many pro and cons for each model, so finance, security, technology and operations must be considered.
What is a public cloud?
Public clouds are the most common type of cloud computing deployment type. The cloud resources such as servers and storage are owned and operated by a third-party cloud service provider and delivered over the internet. With a public cloud, all hardware, software, and other supporting infrastructure is owned and managed by the cloud provider, with Microsoft Azure being an example of a public cloud.
In a public cloud, you share the same hardware, storage, and network devices with other organizations or cloud “tenants,” and you access services and manage your account using a web browser. Public cloud deployments are frequently used to provide web-based email, online office applications, storage, and testing and development environments.
The availability of advanced services in the cloud allows a company to tap into these areas to develop, deploy and operate their applications fasters. Azure cloud, for example, has services such as Anomaly Detectors, Azure Machine Learning, Azure Cognitive Services, Bot Services, Computer Vision and many more – which all allow a company to develop their applications faster and with more capabilities straight out of the box.
Advantages of public clouds:
- No Capex costs—no need to purchase hardware or software; just pay for the service you use.
- No maintenance—your service provider provides the maintenance.
- Near-unlimited scalability—on-demand resources are available to meet your business needs.
- A wealth of services available out of the box.
- Tap into security expertise and AI-driven security.
- High reliability—a vast network of servers protects against failure.
SQL to Azure Migration
A SQL to Azure Migration Assessment will deliver a clear view of the feasibility of migrating infrastructure, the blockers, and the potential path to move on-premise SQL servers to Azure. The assessment is delivered within short written reports and a presentation that allows for Q&A’s with our experts.
What is a private cloud?
A private cloud consists of cloud computing resources used exclusively by one business or organization. The private cloud can be physically located at your organization’s on-site data centre, or it can be hosted by a third-party service provider (Co-location). In a private cloud, the services and infrastructure are always maintained on a private network, and the hardware and software are dedicated solely to your organization.
A private cloud can make it easier for an organization to customize its resources to meet specific IT requirements. Private clouds are often used by government agencies, financial institutions, and any other mid-to large-size organizations with business-critical operations that are seeking enhanced control over their environment.
Advantages of a private cloud:
- More flexibility—your organization can customize its cloud environment to meet specific business needs.
- More control—resources are not shared with others, so higher control and privacy levels are possible.
What is a multi-cloud?
A multi-clouds is a model where an organization utilizes a combination of clouds, which can be two or more public clouds or two or more private clouds. The difference with hybrid clouds is that these models combine multiple clouds of the same type. Most common is the combination of two public clouds, where you would combine Azure with AWS as an example.
Advantages of multi-cloud:
- You can use the best services from each vendor
- Cost optimize where workloads are running
- Better failover and disaster recovery
- Reduce dependency on one cloud vendor
As you deploy to different clouds, one of the main benefits is the ability to utilize the different services and microservices available so that you can build new advanced business supporting applications fast. But this also comes with some challenges, as the cloud vendors typically have different offerings, making the failover and disaster recovery benefits difficult if not impossible to implement.
As each cloud vendor has its own API, portals and security – managing multi-clouds can be challenging. Although 3rd party management frameworks are emerging, the speed of enhancements and changes from each cloud vendor makes those management frameworks obsolete or less useful very fast.
Public clouds and their wealth of services are key to speed
As covered briefly above, the importance of the cloud is often not its ability to provide storage services – but its ability to provide a significant number of services. Those services allow the company to build applications fast and with advanced functionality straight out of the box. The services also allow the management of hybrid identity, site recovery or simply the hosting of a SQL database without the hassle of managing servers.
Examples of services offered from Microsoft Azure is shown in the overview picture below, where you can see the services being split up into different service groups, such as Security and Management, Application Platform, Hybrid Cloud or Intelligence, just to list a few.
Azure AD health monitoring: Provides robust monitoring of your on-premises identity infrastructure, securing a reliable connection to M365 and Microsoft online services.
IOT Hub: A cloud-hosted service that can communicate with millions of IoT devices whilst delivering data in a secure and reliable manner to the backend that needs to process the data.
Azure Container Service allows developers to deploy containers on the Azure public cloud without provisioning any underlying infrastructure. Builds and deploys enterprise high-performance applications.
Azure Cognitive Services: Artificial Intelligence (AI) that can help you build cognitive intelligence into your application. Available as REST or API, so this could even enhance on-premise applications.
Azure Site Recovery: A DRaaS that is used for both native Cloud and Hybrid Architectures to replicate data in a near-constant process, with snapshots that secure recoverability.
As you can see from the picture below, the options are many. Each one has a wealth of functionality as well as technical complexity – if you want to get started with Microsoft Azure or just get more out of it then contact NUDGE IT for an Azure consulting call.